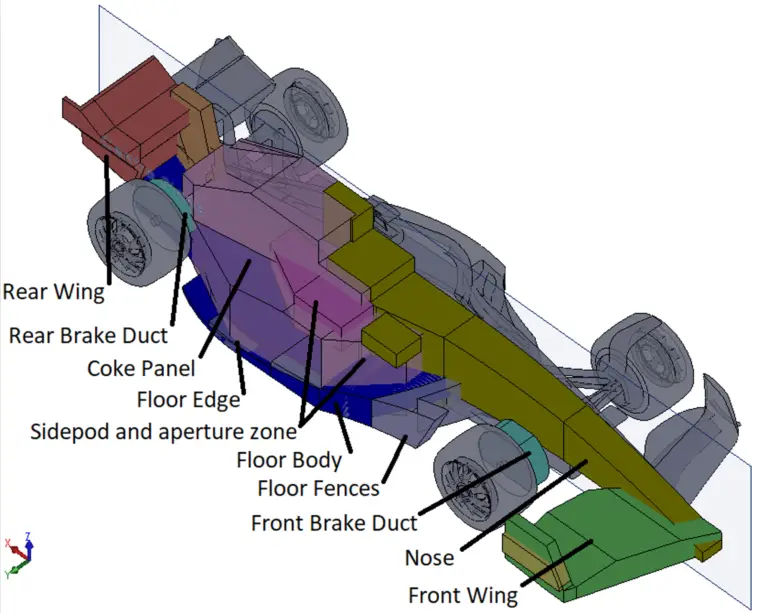
Formula One, also known as F1, is a sport that has captivated motorsport enthusiasts around the world. With its high-speed action, cutting-edge technology, and incredible engineering feats, it is no wonder why F1 has gained such a dedicated following.
At F1Worldwide.com, we strive to provide the latest and most accurate information about this thrilling sport. From race results to driver profiles, we cover it all. One aspect that truly sets F1 apart is the anatomy of an F1 car.
These machines are a marvel of engineering, designed with utmost precision to provide the fastest and safest racing experience possible. The aerodynamic styling and sleek curves of an F1 car are a testament to the hours of wind tunnel testing and computational fluid dynamics analysis that go into their development.
Underneath the surface, an F1 car is a complex network of components. The heart of the car lies in its power unit, which consists of a highly efficient hybrid powertrain. The combination of a turbocharged internal combustion engine and an energy recovery system allows for immense power outputs while also maximizing fuel efficiency.
The chassis of an F1 car is another critical element. Constructed from lightweight and durable materials such as carbon fiber and titanium, the chassis provides the necessary rigidity to withstand the
The anatomy of an F1 car comprises various components, including the chassis, engine, suspension, and aerodynamics. The chassis provides strength and support, while the engine delivers the immense power needed for speed. Suspension ensures stability and control, and aerodynamics maximize downforce and reduce drag. Understanding these elements is crucial to comprehending the intricate design of an F1 car.
The engine is behind the driver. The cars sole purpose is to race in Formula One racing events. Formula One cars are the fastest cars in the world around a race track.
The following is an index of the article
- Formula One Car Chassis design
- Formula 1 Cars Suspension
- Formula 1 Cars Brakes
- Formula 1 Cars Tires And Wheels
- How Formula 1 Cars Are Made
- Are Formula 1 Cars AWD?
- Are Formula 1 Cars The Fastest
- Are Formula 1 Cars Turbocharged?
- Are Formula 1 Cars Electric?
- How Formula 1 Cars Are Transported?
Formula One Car Chassis design
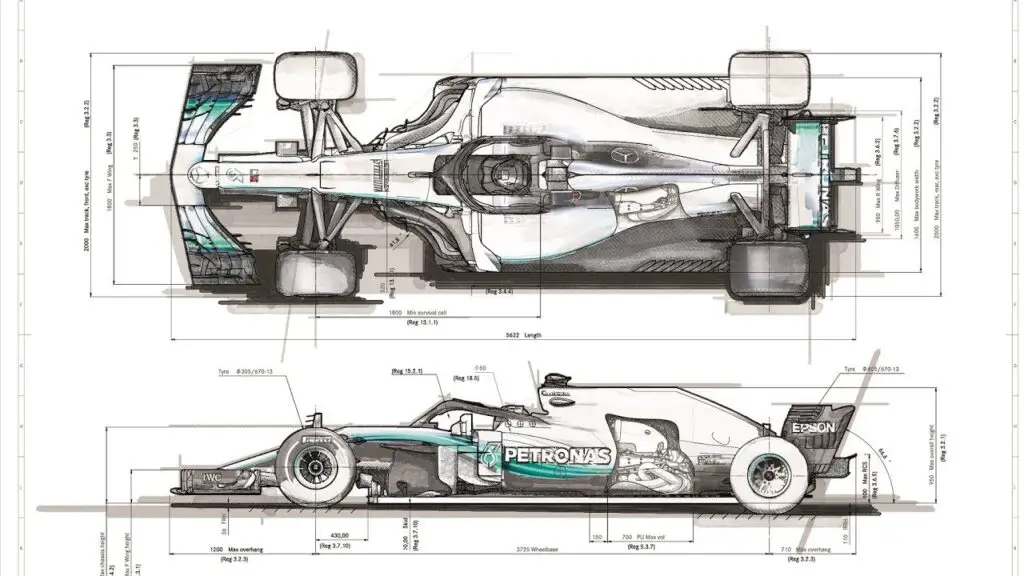
Teams construct Modern-day Formula One cars from composites of carbon fiber and similar ultra-lightweight materials. The minimum weight permissible is 740 kg (1,631 lb.) including the driver but not fuel1. The FIA weighs the cars with dry-weather tires fitted.
The chassis design is subject to strict regulations that aim to ensure safety, performance, and fair competition.
Included in the chassis are the following safety features
- A survival cell that protects the driver from impact and fire.
- A roll-over protection structure (HALO) that prevents the driver’s head from hitting the ground in case of a roll-over.
- A front impact structure that absorbs energy in case of a frontal collision.
The chassis incorporates various aerodynamic devices that generate downforce. This increases the grip of the tires on the road and thus improves cornering performance.
The most prominent of these devices are the front and rear wings, which are adjustable to suit different circuits and conditions. Other aerodynamic features include barge boards, the design of the floor, turning vanes, floor diffusers and rear wing endplates.
Are Formula 1 Cars Hybrids?
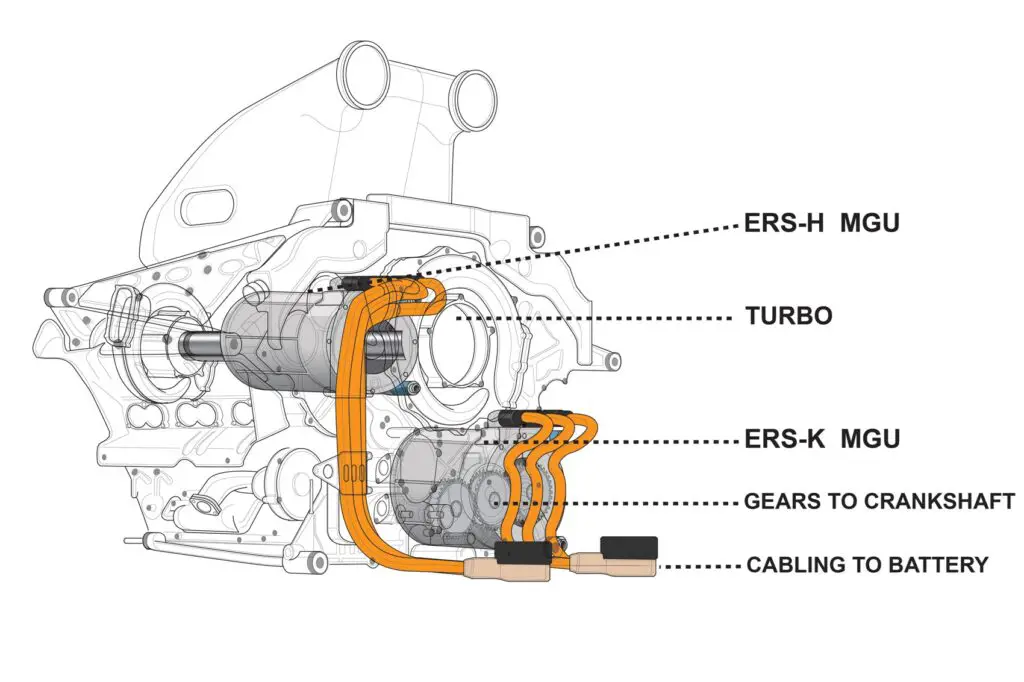
Formula One cars use hybrid engines. These combine a 1.6 liter turbocharged V6 internal combustion engine (ICE) with two electric motor-generator units (MGU).
- The MGU-H connects to the turbocharger.
- The MGU-K connects to the crankshaft
The internal combustion engine can produce up to 750 horsepower (560 kW). The MGU-H and MGU-K can provide an additional 160 horsepower (120 kW) each.
The hybrid system includes
- An energy store (ES) which stores electrical energy recovered from braking and exhaust gas.
- A control electronics (CE) unit that manages the power flow between the ICE, MGU-H, MGU-K and ES1.
The engine and transmission are stressed members of the chassis. They contribute to its rigidity and strength.
Are Formula 1 Cars Manual Or Automatic?
The transmission is a semi-automatic sequential gearbox with eight forward gears and one reverse gear.
The driver shifts gears using paddles on the steering wheel.
The gearbox also incorporates a limited-slip differential that distributes torque between the rear wheels1.
Formula One Car Suspension
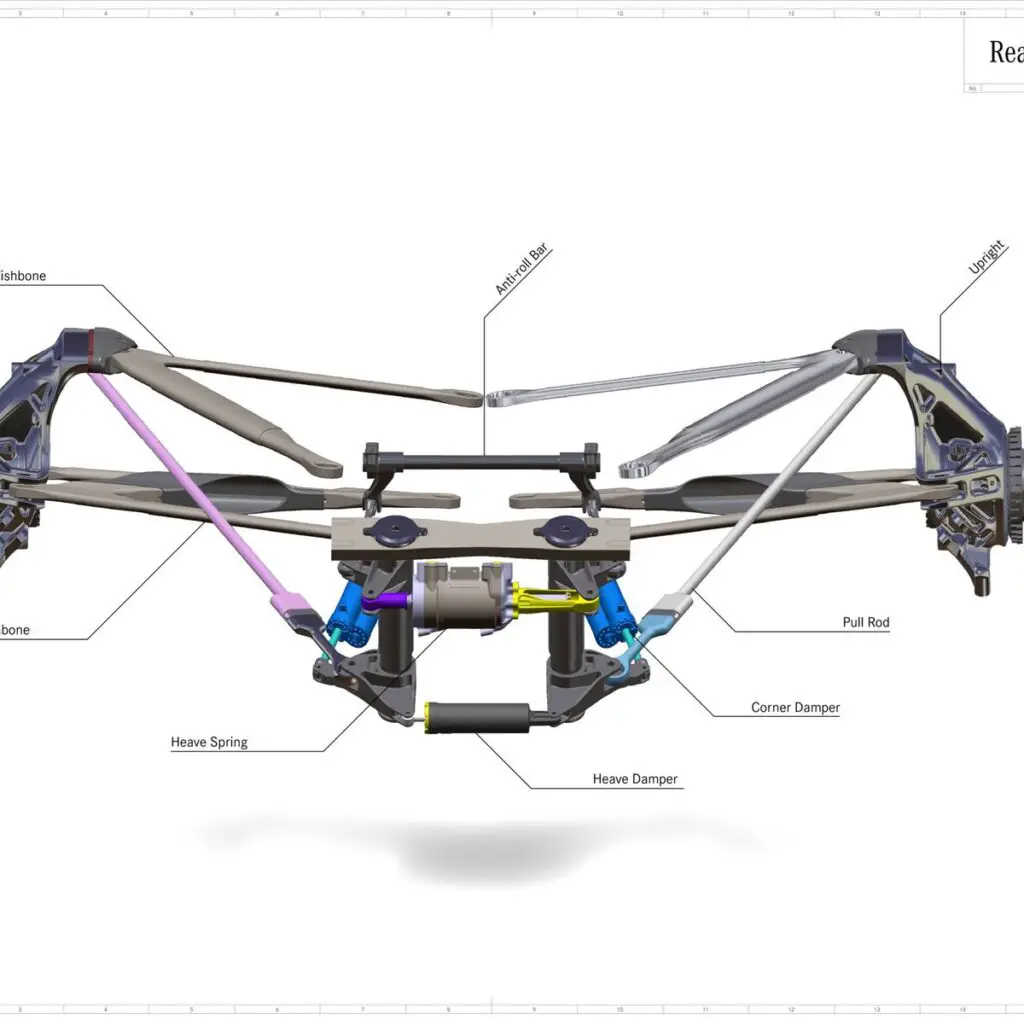
Formula One cars use independent suspension systems. These connect the wheels to the chassis via wishbones, pushrods or pull rods, dampers, and springs.
Teams can adjust the suspension geometry and settings to suit different circuits and conditions.
The suspension also influences the aerodynamics of the car by affecting its ride height and rake angle.
Formula One Car Brakes
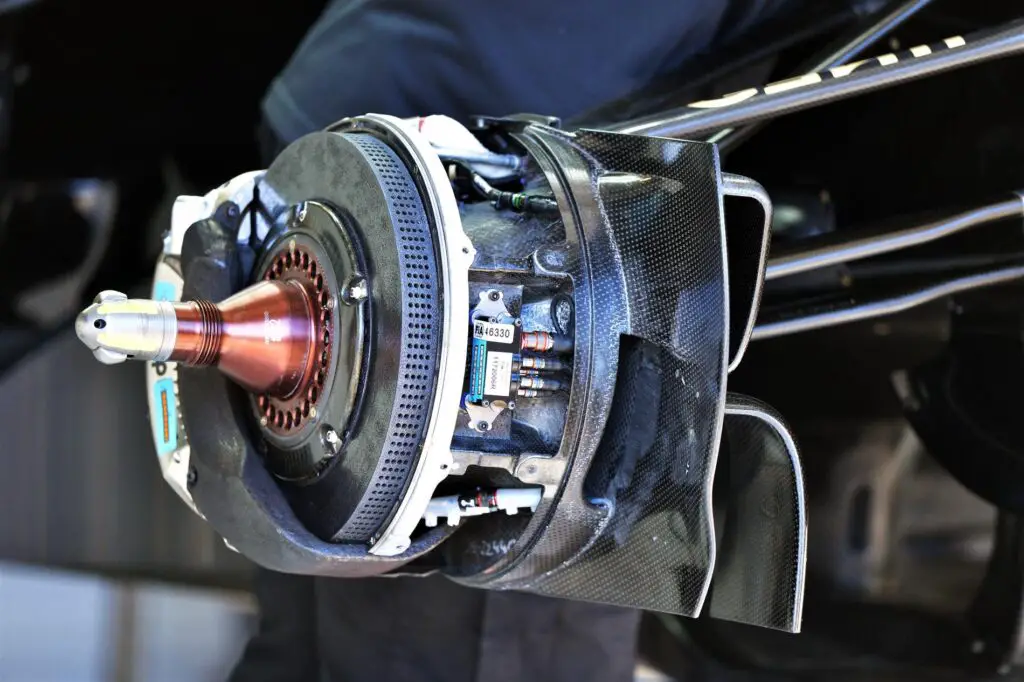
The team make the brakes from carbon fiber composite materials for both the discs and pads.
The brakes operate by a brake-by-wire system that modulates the hydraulic pressure applied to each wheel according to the driver’s input and the available grip.
The brakes recover kinetic energy that is stored in the ES or used by the MGU-K1.
Are Formula One Car Brakes Power Assisted?
There is minimal brake assistance for the driver.
Do Formula 1 Cars Have ABS (Anti-Skid) Brakes?
No the brakes provide no assistance at all.
Formula One Car Tires And Wheels
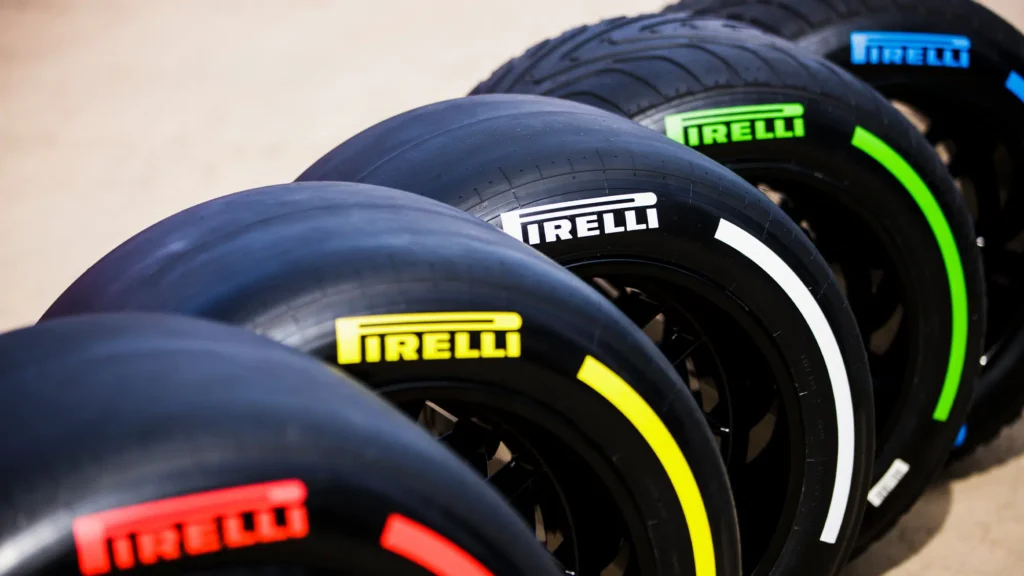

Formula One cars use specially designed tires supplied by Pirelli, the sole tire manufacturer for the championship.
The tires are classified into five compounds with different levels of grip and durability. Pirelli marks eacg compound with a different color on the tire sidewall.
- C1 (hard – White)
- C2 (medium – Yellow)
- C3 (soft – Red)
- C4 (ultra-soft – Purple)
- C5 (hyper-soft – Pink).: white (C1), yellow (C2), red (C3), purple (C4) and pink (C5)1.
The teams have to choose two of these compounds for each race weekend, except for Monaco where they can choose three.
The teams access to two types of wet-weather tires. These are
- Intermediate (green)
- Full wet (blue), which they use in case of rain or damp conditions.
The tires fit on 18-inch wheels with low-profile racing rubber.
The wheel are made of magnesium alloy. The wheels also have sensors that monitor tire pressure and temperature.
Formula One Car Cars Are Made
Formula 1 cars involve cutting edge technology, science, engineering, and creativity. Here is a brief explanation based on the search results:
The cars are built at the teams’ factories, which are divided into several departments that specialize in different aspects of the car.
Formula 1 – Aerodynamics Department
For example, there is an aerodynamics department that designs and tests the wings, bargeboards and other devices that generate downforce;
Formula 1 – Engine Department
an engine department that develops and maintains the hybrid power unit that combines a turbocharged V6 engine with two electric motor-generator units;
Formula 1 – Chassis Department
a chassis department that constructs the carbon fiber composite frame that holds the car together; and so on.
It Takes A Year To Design And Build An F1 Car
It takes a year to build a Formula 1 car.
The process starts with the team leaders discussing the overall concept and strategy for the new car.
Then, a team of designers use computer aided design (CAD) software to create 3D models of the new parts. These can number in the hundreds every day at their peak.
Thet manufacture parts using computer aided manufacture (CAM) machines or hand processing, depending on the complexity and material of the part.
There Are Only Four Engine Manufacturers
The teams make some parts in-house. They buy some from other teams.
Some teams buy their engines and gearboxes from other teams, while others make their own.
The engine suppliers and customers are listed below
| Team | Engine |
|---|---|
| Red Bull Racing | Honda |
| AlphaTauri | Honda |
| Aston Martin | Mercedes |
| McLaren | Mercedes |
| Mercedes | Mercedes |
| Williams | Mercedes |
| Alpine | Renault |
| Haas | Ferrari |
| Alfa Romeo Racing | Ferrari |
| Ferrari | Ferrari |
The regulations standardize or prescribe many parts . These include the wheel aerodynamics, wheel hubs and front floor tray.
When Is The Formula One Car Manufactured?
The teams assemble and test the parts at the factory. Afterwards they ship them to the race track for further testing and fine-tuning.
Engineers constantly updated the car throughout the season. They introduced new parts on a race-by-race basis to improve performance and reliability.
14,500 individual components make up a Formula 1*. Each part is bespoke and unique to each team.
The car has a minimum weight of 740 kg (1,631 lb.) including the driver. The weight does not include fuel. Officials weigh the car with dry-weather tires fitted.
The car can produce up to 910 horsepower (680 kW) from its hybrid power unit and can reach speeds of over 300 km/h (186 mph) on some circuits.
Formula 1 cars are the fastest and most advanced racing cars in the world. Some of the most talented talented and innovative people in motorsport make them.
*This number may vary depending on how you define a component.
Are Formula 1 Cars Street Legal?
No F1 cars are nor street legal. They do not comply with the rule of the road. In addition their low ground clearance would make it impossible to drive them on anything but the smoothest of roads,
Are Formula 1 Cars AWD?
Formula 1 cars are RWD (Rear-wheel drive) with power delivery to the rear wheels only.
AWD systems are illegal in Formula 1, as modern regulations for Formula 1 prohibit more than two driven wheels. For this reason, F1 cars are not AWD and make excellent use of their RWD systems.
How Would AWD Benefit Formula One Car?
AWD systems can provide better traction and performance in wet or slippery conditions, as they distribute power to all four wheels. This can help with acceleration and cornering, especially at low speeds.
AWD systems also have some disadvantages that outweigh their benefits for F1 cars. These include:
- AWD systems are heavy, adding extra weight to the car that can affect its speed and agility.
- AWD systems require all wheels to be the same size, which would reduce the cornering ability of F1 cars that have larger rear wheels and smaller front wheels for optimal steering and power transfer.
- AWD systems are complex and expensive, adding more costs and maintenance issues for the teams2.
How Do Formula One Car Manage Without AWD?
F1 cars rely on their Rear Wheel Drive systems and other technologies to optimize their traction and performance. These include:
- The hybrid power unit, which combines a turbocharged V6 engine with two electric motor-generator units that can provide extra power and recover energy from braking and exhaust gas.
- The brake-by-wire system, which modulates the hydrau c pressure applied to each wheel according to the driver’s input and the available grip.
- The aerodynamic devices, such as wings, and diffusers, that generate downforce that increases the grip of the tires on the road and improves cornering performance.
- The specially designed tires supplied by Pirelli, which have different compounds and colors for different levels of grip and durability.
F1 drivers also rely on their skills and experience to control their cars in various conditions.
They can adjust their driving style and settings to suit different circuits and weather.
The drivers communicate with their engineers and strategists to make informed decisions about tire choices, pit stops and overtaking maneuvers.
F1 cars are lightweight and highly maneuverable. As such they do not need the extra traction of AWD technology.
Instead, they use RWD and the latest technology to achieve incredible speeds and performance.
Are Formula 1 Cars Rear Wheel Drive
Yes, Formula One cars are rear wheel drive.
Are Formula 1 Cars The Fastest
Formula 1 cars are faster than IndyCar and NASCAR cars in terms of top speed and lap time, but IndyCar cars are faster than NASCAR cars.
Formula 1 cars also have better acceleration, cornering, and braking performance than IndyCar and NASCAR cars.
How Fast Are Formula 1 Cars?
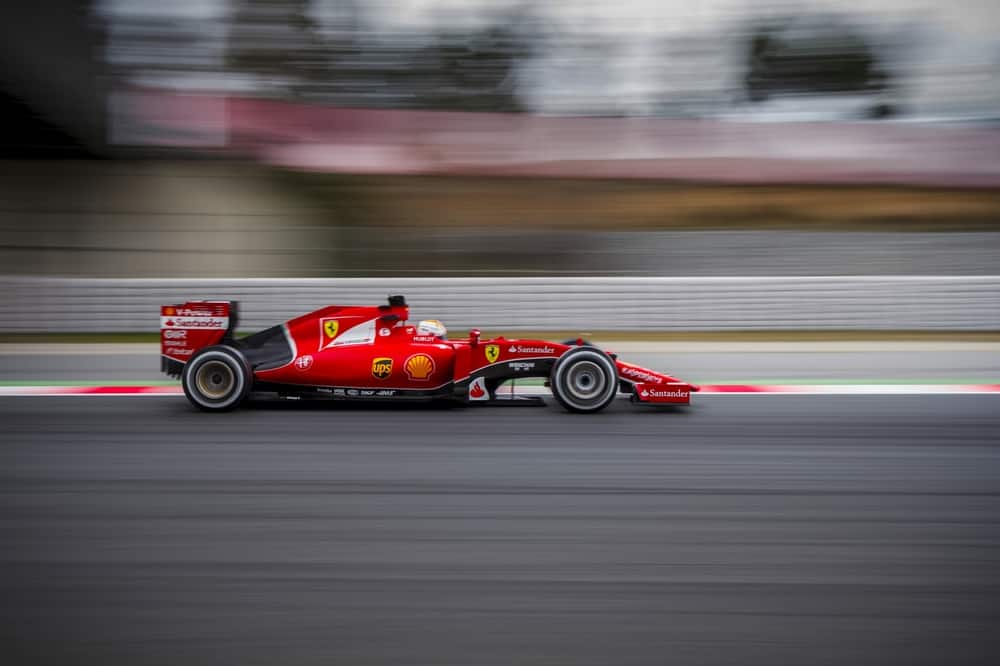

Formula 1 cars can reach a top speed of around 360 km/h (223 mph) in a race, and over 370 km/h (230 mph) in qualifying1.
The fastest ever speed recorded by an F1 car was 397.36 km/h (246.9 mph) by Honda in 2006.
F1 cars can also accelerate from 0 to 60 mph in about 2.6 seconds.
They are lightweight and aerodynamic. They have a hybrid power unit that combines a turbocharged V6 engine with two electric motor-generator units.
F1 cars have large rear wheels and small front wheels for optimal steering and power transfer. F1 cars also have sophisticated aerodynamic devices that generate downforce and improve cornering performance.
How Fast Is IndyCar?
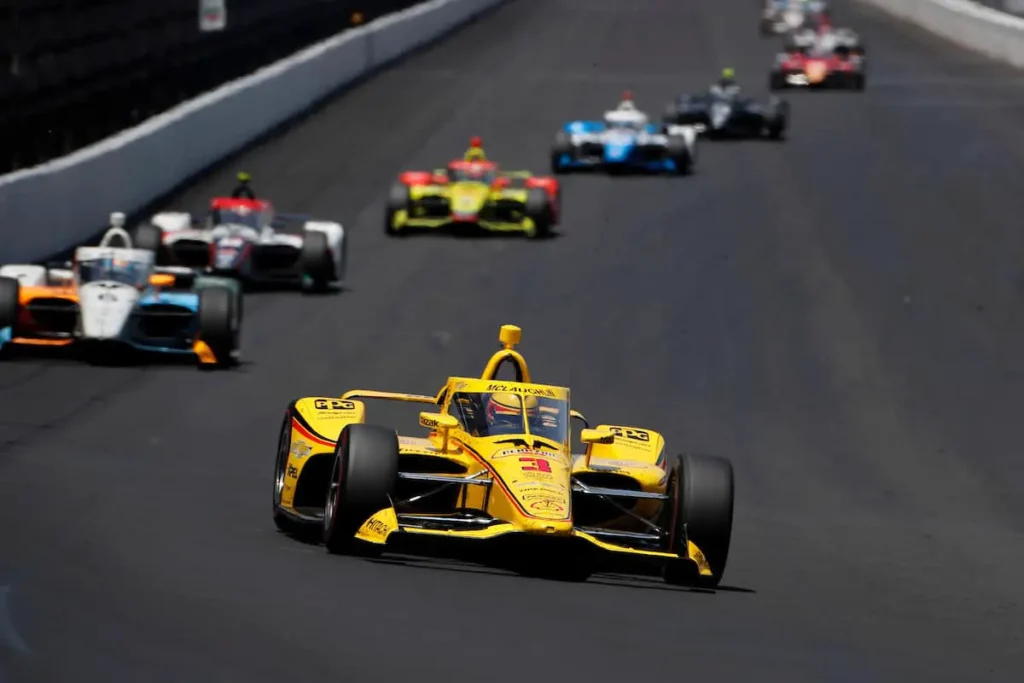

IndyCar cars can reach a top speed of around 373 km/h (231 mph) in a race, which is the fastest out of all three series.
The fastest ever speed recorded by an IndyCar was 385 km/h (239 mph) by Arie Luyendyk in 1996.
IndyCar cars can accelerate from 0 to 60 mph in about 3 seconds. IndyCar cars have open-wheels and are aerodynamic. They have a simpler power unit that consists of a turbocharged V6 engine only.
The cars have all wheels of the same size, which reduces their cornering ability compared to F1 cars. IndyCar cars also have less downforce and grip than F1 cars.
How Fast Are NASCARS
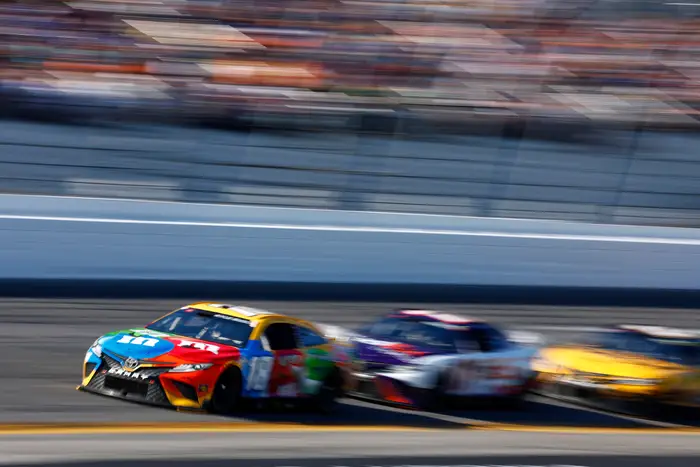

NASCAR cars can reach a top speed of around 321 km/h (200 mph) in a race, which is the slowest out of all three series.
The fastest ever speed recorded by a NASCAR car was 333 km/h (207 mph) by Bill Elliott in 1987.
NASCAR cars can accelerate from 0 to 60 mph in about 3.4 seconds.
NASCAR cars are closed-wheeled and less aerodynamic than F1 and IndyCar cars.
They have a simple power unit that consists of a V8 engine only. NASCAR cars have all wheels of the same size, but they are larger and heavier than F1 and IndyCar wheels.
NASCAR cars also have less downforce and grip than F1 and IndyCar cars.
How Long Are Formula 1 Cars?
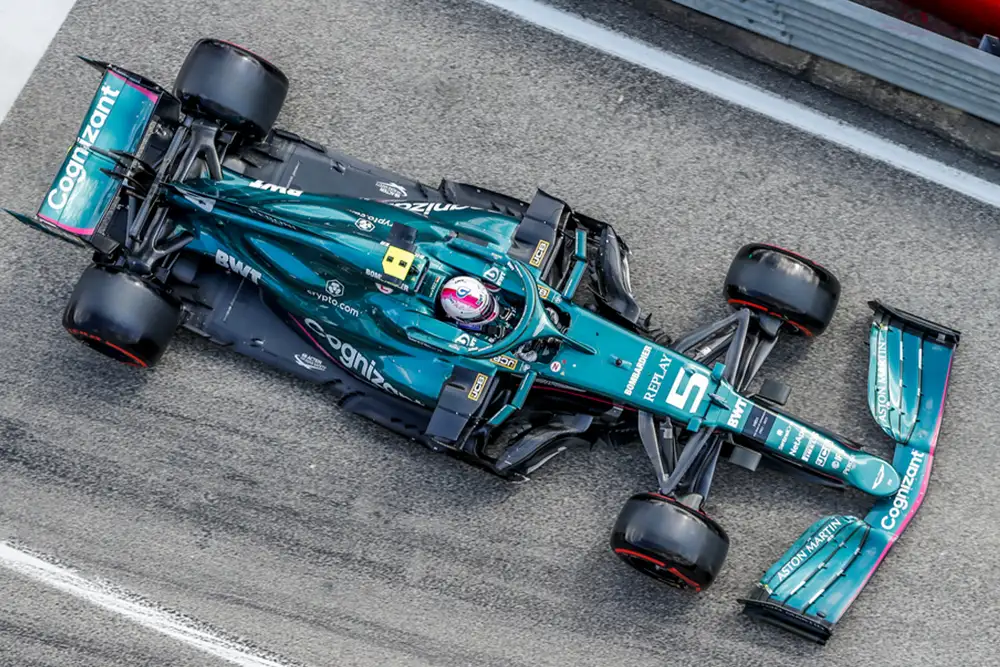

As per the latest rules, F1 car length cannot exceed 5.5 meters. That’s about 18 feet, which means these cars are pretty long. The length of F1 cars has not always been the same. Their length has increased over time, but they were once much shorter.
The width of F1 cars cannot exceed 2 meters as per the latest rules. This regulation was introduced by the FIA in 2017 and made cars wider than ever before.
The height of F1 cars cannot exceed 95 cm as per the latest rules. This regulation was introduced by the FIA in 2022 and made cars lower than ever before.
The weight of F1 cars cannot be less than 796 kg as per the latest rules. This regulation was introduced by the FIA in 2023 and made cars lighter than ever before.
Are Formula 1 Cars Turbocharged?
Formula 1 cars use 1.6 liter four-stroke turbocharged 90 degree V6 double-overhead camshaft (DOHC) reciprocating engines. They were introduced in 2014 and have been developed over the subsequent seasons.
How Formula 1 Engine Work?
A turbocharger is a device that uses exhaust gases to spin a compressor that feeds more air and fuel into the engine’s cylinders. This increases the power and efficiency of the engine2.
Formula 1 cars also use hybrid technology that combines the turbocharged engine with two electric motor-generator units:
- The MGU-Heat is connected to the turbocharger.
- The MGU-Kinetic is connected to the crankshaft (MGU-K).
The MGU-H can recover energy from the turbo or use it to spin the compressor, while the MGU-K can recover energy from braking or use it to assist the engine.
The hybrid system also includes an energy store (ES) that stores electrical energy recovered from braking and exhaust gas, and a control electronics (CE) unit that manages the power flow between the engine, MGU-H, MGU-K and ES.
The turbocharged hybrid engine can produce up to 910 horsepower (680 kW) from its combined power sources.
Are Formula 1 Cars Electric?
The answer is no, Formula 1 cars are not electric. They are gasoline-powered vehicles that use a hybrid system to boost their performance.
Formula 1 cars use 1.6 liter four-stroke turbocharged 90 degree V6 double-overhead camshaft (DOHC) reciprocating engines that run on 87-102 octane gasoline, which is similar to that used in standard road cars1.
The gasoline engine can produce up to 750 horsepower (560 kW).
Formula 1 cars also use a hybrid system that combines the gasoline engine with two electric motor-generator units: one connected to the turbocharger (MGU-H) and one connected to the crankshaft (MGU-K).
The MGU-H can recover energy from the turbo or use it to spin the compressor, while the MGU-K can recover energy from braking or use it to assist the engine.
The hybrid system can provide an additional 160 horsepower (120 kW) each.
The hybrid system also includes an energy store (ES) that stores electrical energy recovered from braking and exhaust gas. It includes a control electronics (CE) unit that manages the power flow between the engine, MGU-H, MGU-K and ES.
The electric motor-generator units and the energy store are not used to power the car independently of the gasoline engine.
They are only used to boost the performance of the car by providing extra power and efficiency. If the electric supply fails, the car will automatically stop1.
Formula 1 cars are not electric vehicles; rather, they are gasoline-powered vehicles with an electric boost.
How Formula 1 Cars Are Transported?
Formula 1 cars are transported by road, air, or sea, depending on the distance and time between races.
Formula 1 cars are built at the teams’ factories, which are mostly located in Europe or the U.K. The cars and equipment are then packed into specially-built containers and trucks that can carry up to 40 tons of cargo.
The teams have to transport thousands of kilograms of equipment, including multiple cars, spare parts, and other essential items, from one location to another in a matter of days.
The process of transporting Formula 1 cars requires meticulous planning and coordination. The teams rely on different modes of transport to ensure that everything arrives on time.
F1 Car Transport – Road
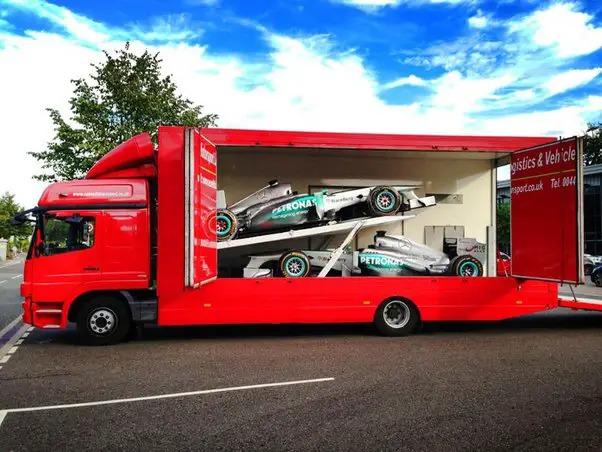

For races that take place in Europe, teams usually transport their cars and equipment by road using large trucks.
This is the easiest and most cost-effective way to move F1 cars and equipment within the same continent.
F1 Car Transport – Air
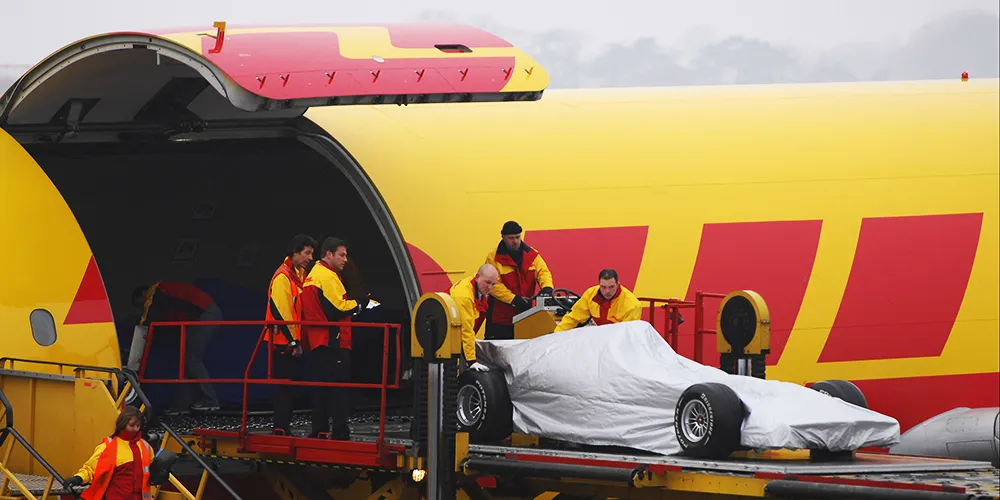

For races that take place outside Europe, teams usually transport their cars and equipment by air using cargo planes.
This is the fastest and most reliable way to move F1 cars and equipment across different continents, but also the most expensive.
Teams have to secure cargo space on planes and properly package their cars and equipment to ensure they arrive safely at their destination.
Teams also have to coordinate the logistics of air transport, including arranging pick-up and delivery times, loading, and unloading planes, and paying various fees.
F1 Car Transport – Sea
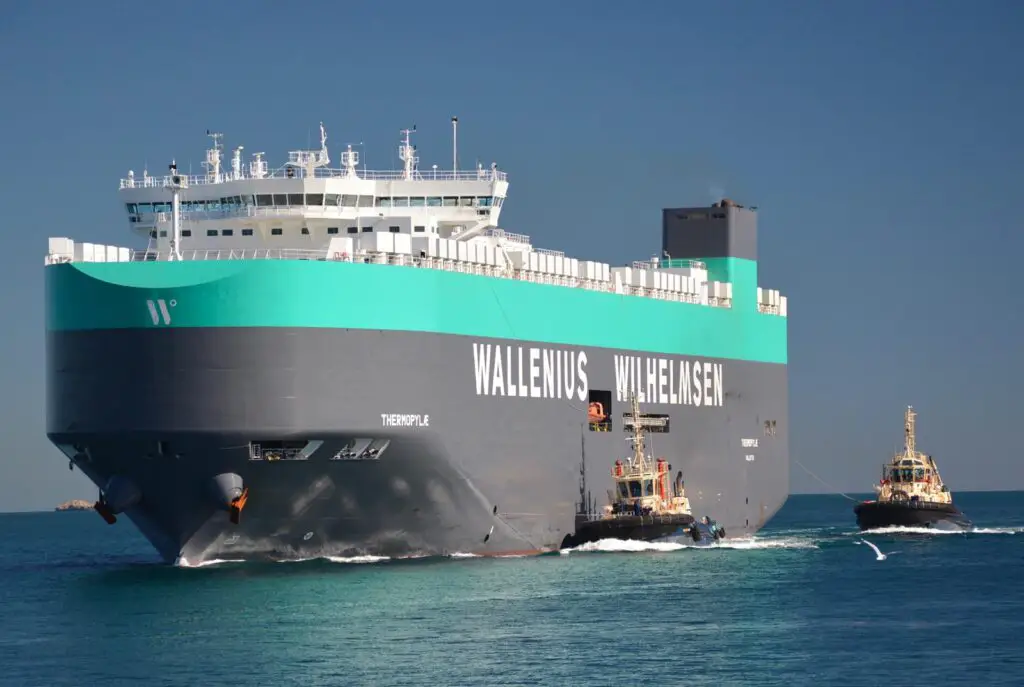

For races that take place far away from Europe, teams may also use sea transport to ship some of their cars and equipment by boat.
This is the slowest but most cost-effective way to move F1 cars and equipment between countries. It is also the most risky due to potential delays or damage.
Teams mainly use sea transport for non-critical equipment, such as tools, car jacks, and spare parts.
Teams also have to coordinate the logistics of sea transport, including booking containers, clearing customs, and paying various fees.
Transporting Formula 1 cars between races is a complex and costly process that requires the expertise of experienced logistics professionals.
It is a critical part of the sport’s operations that ensures that the cars and equipment arrive at each race in peak condition.