Formula 1 is the pinnacle of motorsport, where the best drivers and teams compete for glory and fame. But what makes these cars so fast and powerful? The answer lies in their engines, which are among the most advanced and complex machines in the world. But how much power do F1 engines produce? And how do they achieve such high levels of performance?
1050 Horsepower in 2023
The short answer is that F1 engines produce around 1050 horsepower in 2023. This is the maximum power output of the internal combustion engine (ICE). It is only one main component of the F1 power unit. The ICE is a 1.6-litre turbocharged V6 engine that can rev up to 15,000 rpm.
However, this is not the only source of power for an F1 car. The F1 power unit also includes two energy recovery systems (ERS). These are electrical devices that harvest and store energy from the car’s braking and exhaust. The ERS consists of two components: the motor generator unit-kinetic (MGU-K) and the motor generator unit-heat (MGU-H).
The MGU-K recovers kinetic energy from the car’s braking and converts it into electrical energy. The recovered energy is stored in a battery. The MGU-K can also use this energy to provide an extra boost of 160 horsepower. The problem is the additional boost is only available for 33 seconds per lap.
The MGU-H recovers thermal energy from the car’s exhaust and converts it into electrical energy. It is used to power the MGU-K or the turbocharger. The MGU-H can also control the speed of the turbocharger, which helps to reduce turbo lag and improve engine efficiency.
The combined power output of the ICE and the ERS is around 1210 horsepower. The power is not always available or used by the drivers. This is because they have to manage their fuel consumption and battery charge throughout the race. The drivers can also adjust their engine modes, which affect the power delivery and performance of their cars.
The Evolution of F1 Engines
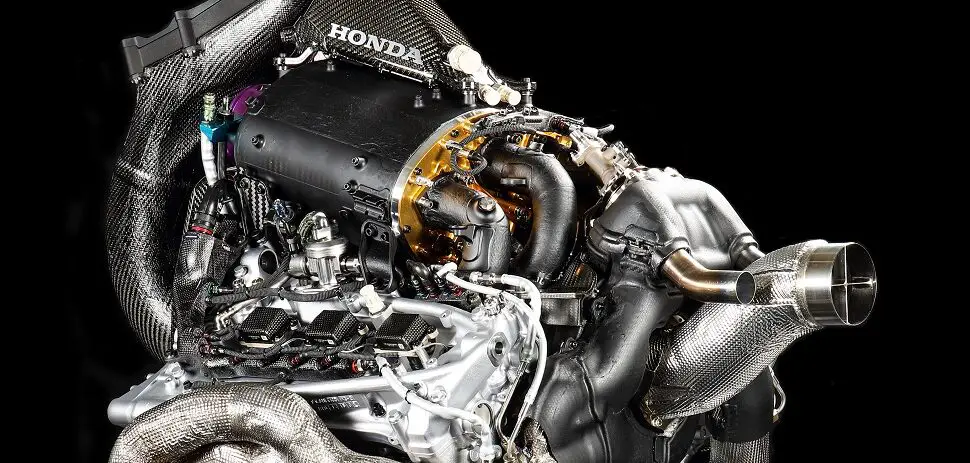
F1 engines have undergone many changes and developments over the years, as the sport has adapted to different regulations and challenges. The history of F1 engines can be divided into different eras, based on their configuration and specifications.
The Early Engines
The first era of F1 engines was from 1950 to 1960, when naturally aspirated engines with various cylinder numbers and displacements were used. The most common engines were four-cylinder, six-cylinder, and eight-cylinder engines, with displacements ranging from 1.5 liters to 4.5 liters.
The Second Generation F1 Engines
The second era of F1 engines was from 1961 to 1986, when naturally aspirated engines with a maximum displacement of 3 liters were used. The most common engines were eight-cylinder and twelve-cylinder engines, with some exceptions such as six-cylinder and sixteen-cylinder engines.
The Third Generation F1 Engines
The third era of F1 engines was from 1987 to 1988, when turbocharged engines with a maximum displacement of 1.5 litres were used. The most common engines were four-cylinder and six-cylinder engines, with some exceptions such as five-cylinder engines.
The Fourth Generation F1 Engines
The fourth era of F1 engines was from 1989 to 1994, when naturally aspirated engines with a maximum displacement of 3.5 liters were used. The most common engines were eight-cylinder and ten-cylinder engines, with some exceptions such as twelve-cylinder engines.
The Fifth Generation Of F1 Engines
The fifth era of F1 engines was from 1995 to 2005, when naturally aspirated engines with a maximum displacement of 3 liters were used. The most common engines were ten-cylinder engines, with some exceptions such as eight-cylinder and twelve-cylinder engine.
The Sixth Generation Of F1 Engines
The sixth era of F1 engines was from 2006 to 2013, when naturally aspirated engines with a maximum displacement of 2.4 liters were used. The most common engines were eight-cylinder engines, with some exceptions such as ten-cylinder and twelve-cylinder engines.
The Seventh Generation Of F1 Engines
The seventh era of F1 engines is from 2014 to present, when hybrid turbocharged engines with a maximum displacement of 1.6 liters are used.
References
Honda sign new Red Bull contract leaves Porsche rumors dead | thejudge13

