In the fast-paced world of F1 Racers, the pursuit of speed and innovation has always been at the forefront. Over the years, the sport has seen an incredible evolution, with cutting-edge technology playing a pivotal role. It has shaped the performance and capabilities of these high-speed machines.
From the early days of simple, open-wheeled cars to the sophisticated and aerodynamically advanced vehicles of today, Formula 1 has witnessed a remarkable transformation. This evolution has not only pushed the boundaries of engineering but has also revolutionized the way races are won.
In this article, we delve into the fascinating journey of F1 racers and explore the role that technology has played. Join us as we uncover the innovations, advancements, and breakthroughs that have made Formula 1 a thrilling spectacle.
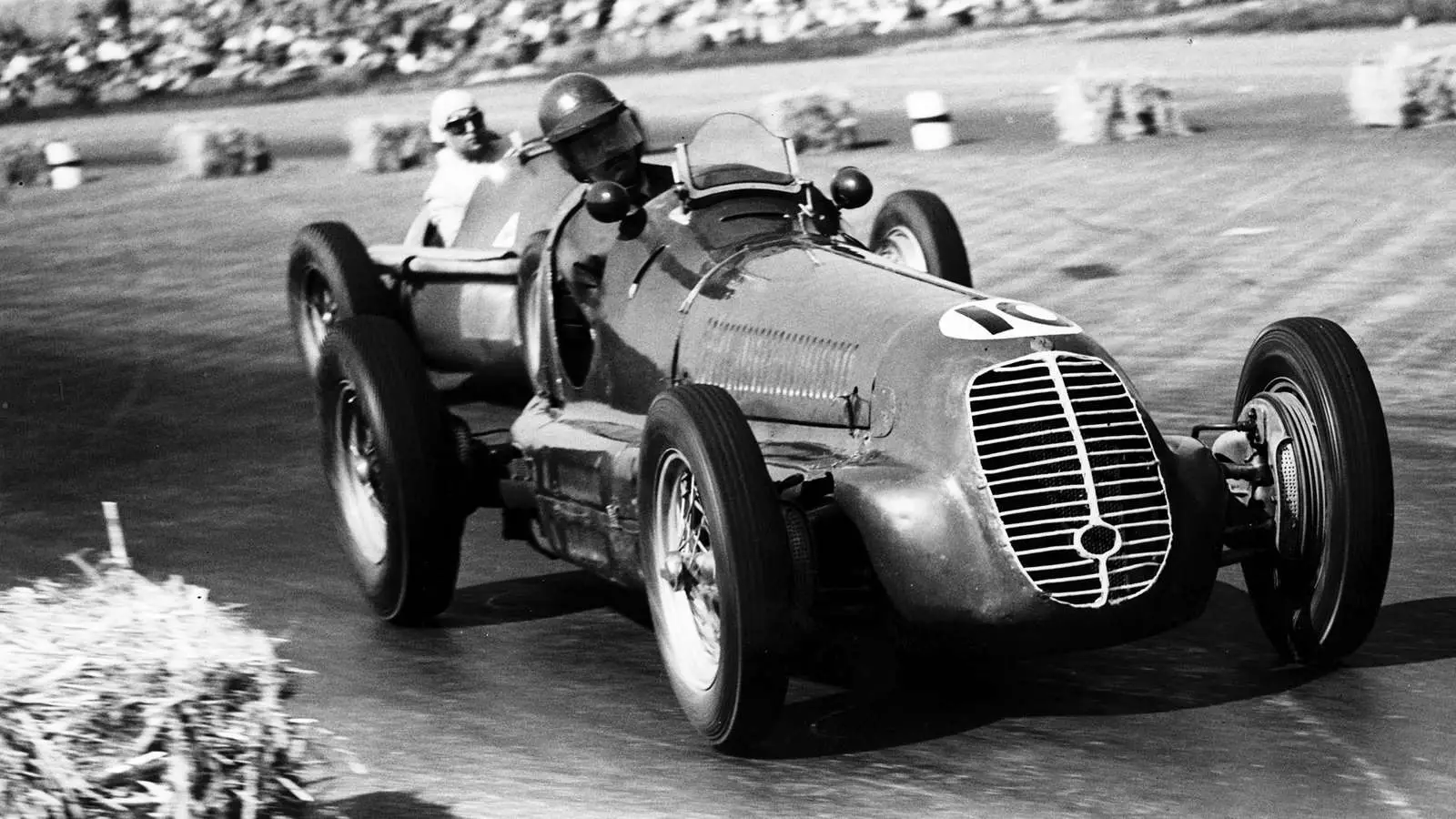
The Early Years of F1 Racers
The roots of F1 Racing can be traced back to the early years of motorsport. It harks back to the last decade of the 19th century.
During this time, the cars were simple, open-wheeled designs with limited horsepower. These early F1 racers were essentially modified versions of road cars, with minimal aerodynamic enhancements and basic safety features.
However, even in these early years, the quest for speed and performance was evident. Drivers pushed the limits of their machines, showcasing their skill and bravery on the track.
While technology was limited compared to today’s standards, it laid the foundation for the advancements that were to come.
As the popularity of Grand Prix racing grew, so did the need for more advanced and specialized race cars. Manufacturers began to invest in research and development, experimenting with new materials and designs to gain a competitive edge. This marked the beginning of the technological revolution in Formula 1 racing.
The Impact of technology on F1 Racers
The introduction of new technologies in Formula 1 racing had a profound impact on the sport. As engineers and designers pushed the boundaries of what was possible, the performance and capabilities of F1 racers improved dramatically.
F1 was formalized from the 1950s onwards. Advancements in aerodynamics, engine technology, and data analytics transformed the sport.
Aerodynamics and its Role in F1 Racers
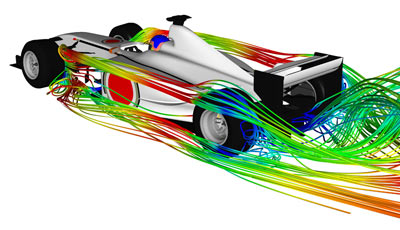
One of the most significant areas of technological advancement in Formula 1 racing is aerodynamics. The science of airflow and downforce became crucial in maximizing the performance of these high-speed machines.
As engineers gained a deeper understanding airflow, they began to design shapes that minimized drag and generated downforce. This allowed the cars to maintain stability at high speeds and negotiate corners with greater precision.
The introduction of wings, diffusers, and other aerodynamic components revolutionized the sport. These enabled F1 racers to achieve unprecedented levels of grip and cornering speeds.
To optimize aerodynamic performance, teams started using wind tunnels and computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations to fine-tune their designs.
These tools allowed engineers to study the airflow around the car and make adjustments to maximize performance. The constant pursuit of aerodynamic efficiency became a defining characteristic of Formula 1 racing. Teams invested significant resources in developing innovative solutions to gain a competitive advantage.
Engine Technology Advancements in F1 Racers
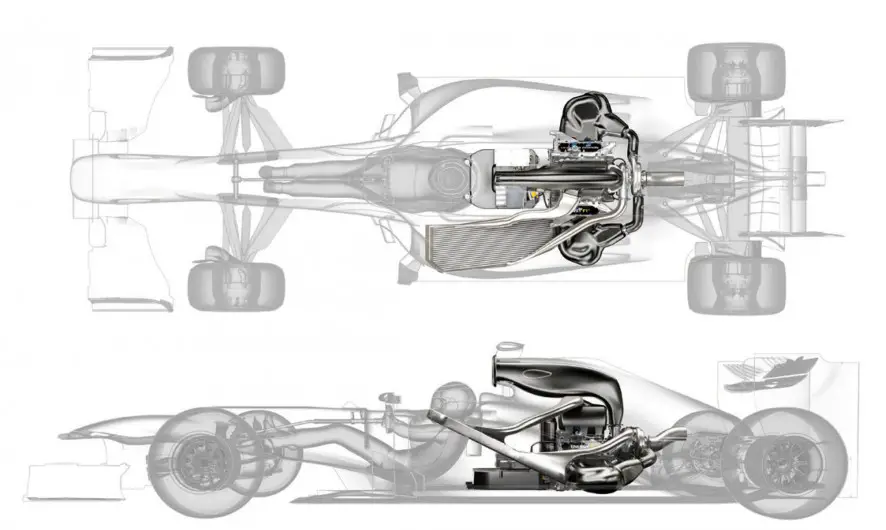
Another area where technology has had a profound impact on Formula 1 racing is engine development.
From the early days of naturally aspirated engines to the introduction of turbochargers and hybrid power units, the evolution of F1 engines has been nothing short of remarkable. As teams sought to extract more power and efficiency from their engines, they turned to advanced technologies and engineering solutions.
In recent years, the introduction of hybrid power units has revolutionized the sport. These power units combine a traditional internal combustion engine with an electric motor, enabling teams to harness energy from braking and deploy it for additional power.
This hybrid technology not only improves fuel efficiency but also provides an extra boost of power during overtaking maneuvers. The integration of these systems requires sophisticated control algorithms and software, showcasing the role of digital technology in enhancing performance.
The Role of Data and Analytics in F1 Racers

Data and analytics have become integral to the success of Formula 1 teams. With sensors and telemetry systems embedded in the cars, teams can collect vast amounts of data during races and testing sessions.
This data is then analyzed to gain insights into the car’s performance, driver behavior, and race strategies. By leveraging data analytics, teams can make informed decisions and optimize their performance on the track.
Teams use advanced algorithms to analyze data in real-time, providing engineers and strategists with valuable information during races.
From tire wear and fuel consumption to aerodynamic performance and pit stop strategies, every aspect of the race is analyzed to gain a competitive advantage.
The ability to process and interpret data quickly has become a key differentiator in Formula 1 racing, allowing teams to make split-second decisions that can determine the outcome of a race.
Safety Innovations in F1 Racing
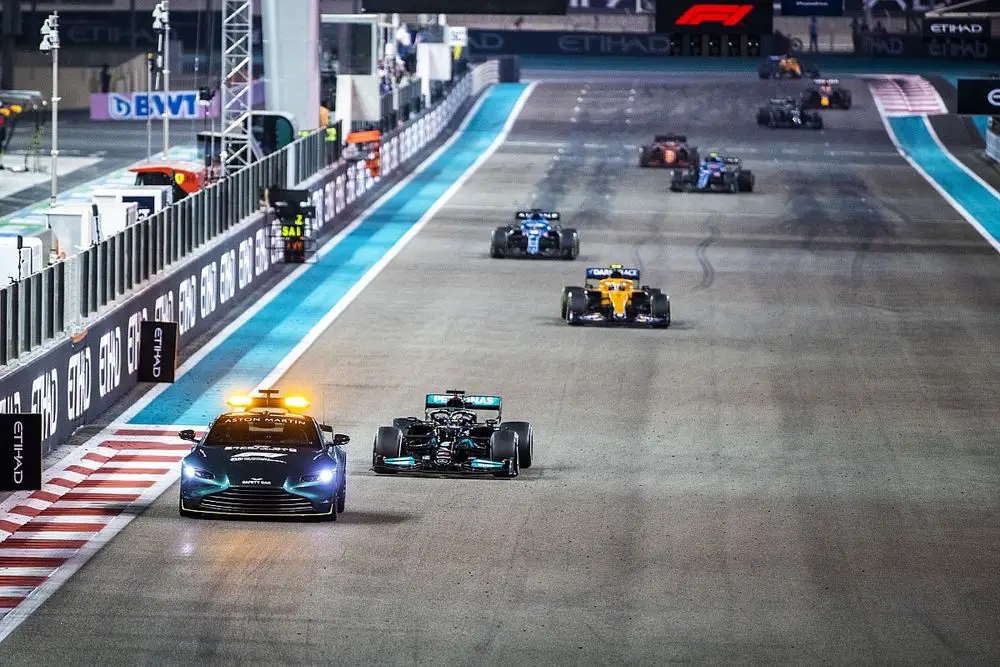

While speed and performance have always been the focus of Formula 1 racing, safety has also played a significant role in its evolution.
Over the years, the sport has witnessed several tragic accidents that prompted a renewed focus on driver safety. As a result, Formula 1 has become a pioneer in implementing safety innovations that have since been adopted by other motorsports.
From the introduction of safety harnesses and roll cages to the development of crash-resistant materials and impact-absorbing barriers, Formula 1 has made significant strides in improving driver safety.
Advanced helmet designs, fireproof suits, and the introduction of the Halo cockpit protection system have further enhanced the safety of F1 racers.
The ongoing commitment to safety reflects the sport’s dedication to protecting its drivers while pushing the boundaries of performance.
The Future of Technology in F1 Racing
As Formula 1 continues to evolve, technology will undoubtedly play a crucial role in shaping its future. With advancements in areas such as artificial intelligence, electric propulsion, and autonomous driving, the sport is poised for further transformation.
As sustainability and environmental concerns gain prominence, Formula 1 is exploring ways to reduce its carbon footprint and embrace cleaner technologies. The integration of electric powertrains and the development of sustainable fuels are just some of the areas being explored.
Furthermore, advancements in virtual reality and augmented reality technologies could redefine the viewing experience for fans, allowing them to immerse themselves in the race from the comfort of their homes.
The potential for real-time data visualization and enhanced interactivity could create a new level of engagement for spectators.
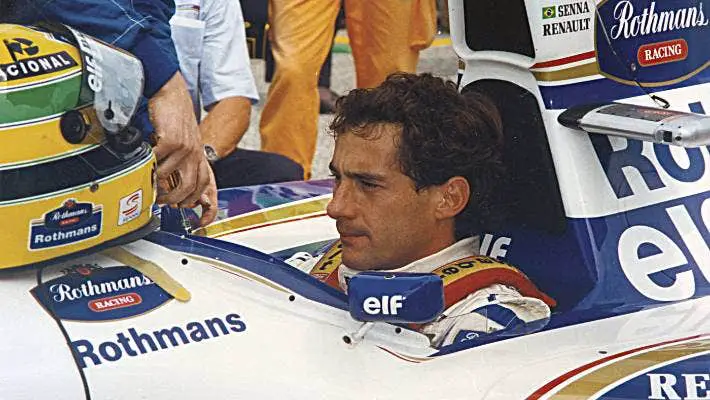
Famous F1 Racers and Their Impact on the Sport

![Michael Schumacher [1994]](https://f1worldwide.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Michael-Schumacher-1994-1024x576.jpeg)
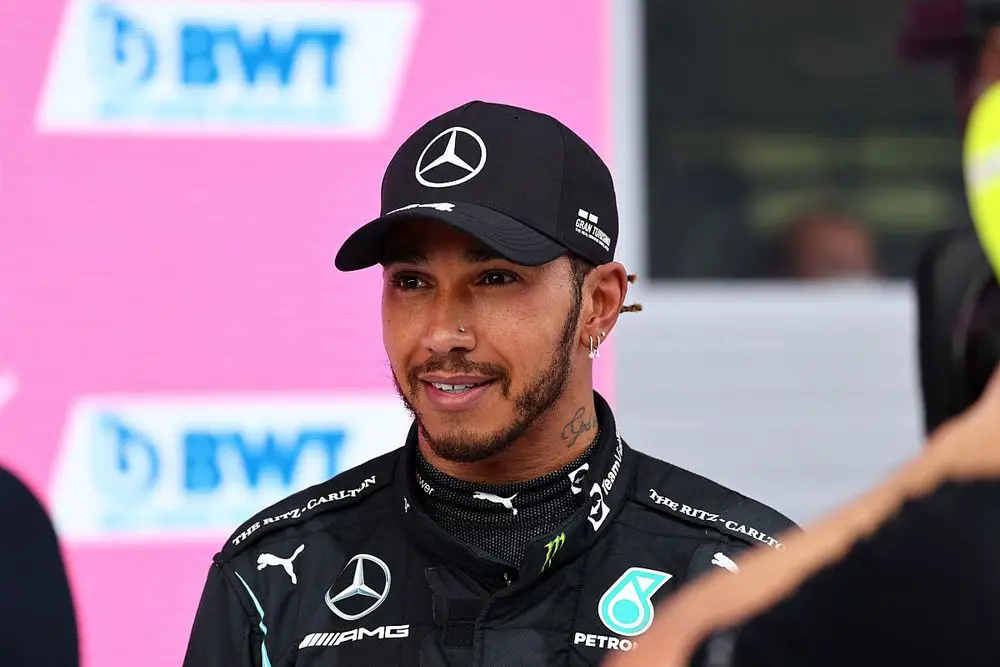

Throughout the history of Formula 1 racing, there have been several iconic drivers who have left an indelible mark on the sport.
From the legendary Ayrton Senna to the dominant Michael Schumacher and the current superstar Lewis Hamilton, these drivers have showcased their skill and determination. They have also been remarkable ambassadors for the sport.
Their impact extends beyond the track, inspiring a new generation of racers and fans alike.
From their driving techniques to their ability to adapt to changing technologies and race strategies, these F1 legends have shaped the sport in numerous ways.
Their records, achievements, and rivalries have become part of the sport’s rich history, fueling the passion and excitement that Formula 1 continues to generate.
Conclusion: The Ongoing Evolution of F1 racing
Formula 1 racing has come a long way since its humble beginnings. From the early years of simple, open-wheeled cars to the technologically advanced machines of today, the sport has witnessed an incredible evolution.
Technology has played a pivotal role in shaping the performance, capabilities, and safety of these high-speed machines. From advancements in aerodynamics and engine technology to the use of data analytics and safety innovations, Formula 1 has embraced cutting-edge solutions to push the boundaries of what is possible.
As the sport looks to the future, technology will continue to drive its evolution. From sustainable powertrains to immersive viewing experiences, Formula 1 is poised for further transformation. As fans eagerly await the next race, they can rest assured that the captivating journey of F1 racers will continue to be shaped by the relentless pursuit of speed, innovation, and state-of-the-art engineering.
FAQ’s
What F1 Technology made it to Road Cars?
Several technologies developed in Formula 1 have successfully made their way to road cars, contributing to advancements in automotive innovation. Some notable examples include:
- KERS (Kinetic Energy Recovery System): Initially designed to recover and store energy during braking in Formula 1, KERS technology has been adapted for road cars. Hybrid and electric vehicles often feature regenerative braking systems that harness and store kinetic energy, improving overall efficiency.
- Carbon Fiber Construction: Formula 1 pioneered the use of lightweight and robust carbon fiber composites in car construction. This material has since been adopted in the production of high-performance road cars, enhancing both safety and fuel efficiency.
- Aerodynamics: Cutting-edge aerodynamic concepts, such as those developed for Formula 1 cars to improve downforce and reduce drag, have influenced the design of road cars. Manufacturers incorporate aerodynamic principles to enhance fuel efficiency and overall performance.
- Semi-Automatic Gearboxes: The seamless and rapid gear changes seen in Formula 1 have influenced the development of semi-automatic and dual-clutch transmissions in road cars, providing drivers with smoother and more efficient gear shifts.
- Advanced Materials and Alloys: The quest for lightweight yet durable materials in Formula 1 has led to the use of advanced alloys and materials. Many road cars now incorporate these innovations to achieve a balance between performance, safety, and fuel efficiency.
- Data Telemetry and Connectivity: The sophisticated data telemetry systems used in Formula 1 for real-time monitoring of car performance have inspired connected technologies in road cars. Modern vehicles often feature advanced connectivity options and in-car data systems.
What is the Engineering behind F1 Cars?
Formula 1 cars are marvels of engineering, blending cutting-edge technology and precision craftsmanship. The engineering behind F1 cars is a multi-faceted process that involves various elements:
- Aerodynamics: F1 cars are meticulously designed to slice through the air with minimal resistance. Advanced aerodynamics, including wings, diffusers, and bargeboards, optimize downforce for superior grip on the track while minimizing drag for higher speeds.
- Materials and Construction: F1 cars utilize lightweight materials like carbon fiber and titanium to enhance strength without compromising weight. Monocoque chassis, designed as a single shell, provide a rigid yet lightweight structure, ensuring safety and performance.
- Power Unit: The heart of an F1 car is its power unit, a complex assembly that includes the hybrid combination of a turbocharged V6 engine, Energy Recovery System (ERS), and Energy Store. This hybrid setup maximizes power output while meeting stringent fuel efficiency regulations.
- Suspension Systems: Advanced suspension systems, featuring push-rod or pull-rod designs, optimize handling and responsiveness. Engineers meticulously tune the suspension to adapt to different track conditions and enhance overall stability.
- Braking Systems: F1 cars employ state-of-the-art carbon-ceramic brake discs and advanced brake-by-wire systems. These technologies provide exceptional stopping power and allow for precise control during high-speed racing.
- Data Telemetry: F1 cars generate vast amounts of real-time data, capturing everything from engine performance to tire wear. Data telemetry systems relay this information to the team’s engineers, enabling real-time analysis and strategic decision-making during races.
- Tires: Tire technology is critical in F1, with bespoke tire compounds tailored for specific tracks and weather conditions. Engineers work closely with tire manufacturers to optimize grip, durability, and performance.
- Transmission and Gearbox: F1 cars feature highly sophisticated gearbox systems, often semi-automatic or dual-clutch, enabling rapid and seamless gear changes. These gearboxes are designed for optimal power delivery and efficiency.
- Steering and Control Systems: Steering in F1 cars is highly responsive, often using electronic systems
What Technology is Used in F1?
Formula 1 is at the forefront of technological innovation, incorporating cutting-edge advancements that define the pinnacle of motorsport. Key technologies used in F1 include:
- Aerodynamics: F1 cars feature advanced aerodynamic components such as wings, diffusers, and bargeboards to optimize downforce and reduce drag for maximum performance.
- Power Unit: The hybrid power unit comprises a turbocharged V6 engine, Energy Recovery System (ERS), and Energy Store, showcasing state-of-the-art engineering for a potent yet fuel-efficient powerplant.
- Materials: Lightweight and durable materials like carbon fiber, titanium, and advanced alloys are employed in constructing F1 cars to enhance strength without compromising weight.
- Data Telemetry: Real-time data telemetry systems capture and transmit a wealth of information, from engine performance to tire data, enabling teams to make strategic decisions during races.
- Tire Technology: F1 tires are a technological marvel, with bespoke compounds tailored for specific tracks and conditions, providing optimal grip and performance.
- Suspension Systems: Advanced suspension systems, often featuring push-rod or pull-rod designs, are finely tuned to adapt to different track conditions, optimizing handling and stability.
- Braking Systems: Carbon-ceramic brake discs and sophisticated brake-by-wire systems deliver exceptional stopping power while allowing for precise control during high-speed racing.
- Transmission: F1 cars utilize highly sophisticated transmission systems, often semi-automatic or dual-clutch, for rapid and seamless gear changes, optimizing power delivery.
- Steering and Control Systems: Responsive steering systems, coupled with electronic control systems, ensure precise and efficient control of the car, translating driver inputs into seamless movements on the track.
- Safety Innovations: F1 is a leader in safety technology, with features like the Halo cockpit protection system, designed to enhance driver safety in the event of an impact.
What Software do F1 Teams Use?
Formula 1 teams leverage a sophisticated array of software solutions to gain a competitive edge in the highly dynamic world of motorsport. Key software applications used by F1 teams include:
- Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD): Teams employ CFD software to simulate and analyze the aerodynamics of their cars, optimizing designs for maximum performance and efficiency.
- Simulation Software: Advanced simulation tools are utilized to model various race scenarios, test car setups, and predict performance outcomes. This aids in strategic decision-making and fine-tuning race strategies.
- Data Analytics: F1 teams rely on data analytics software to process vast amounts of telemetry data collected during races and testing. This enables real-time performance analysis and adjustments.
- Race Strategy Software: Teams utilize specialized software to develop and refine race strategies, considering factors such as tire degradation, fuel efficiency, and competitor behaviors.
- Car Performance Modeling: Software is employed to create detailed virtual models of the car, allowing engineers to simulate and optimize various components for enhanced performance.
- Communication and Collaboration Tools: Teams use collaborative platforms and communication software to streamline interactions among engineers, designers, and strategists, fostering efficient collaboration.
- Vehicle Dynamics Simulation: This software helps teams understand how the car will behave under different conditions, allowing for adjustments to optimize handling, balance, and overall performance.
- Supply Chain Management Software: To ensure timely availability of parts and components, teams utilize supply chain management tools to track inventory, orders, and logistics.
- Additive Manufacturing Software: F1 teams embrace additive manufacturing technologies, and the associated software facilitates the design and production of intricate and lightweight components using 3D printing.
- Cybersecurity Solutions: With the increasing digitization of race operations, F1 teams prioritize cybersecurity software to protect sensitive data and ensure the integrity of their systems.
What is the Green Paint that One Sometimes sees on Formula One cars?

The green paint often seen on Formula 1 cars is a substance called flo-vis paint, short for flow visualization paint. It is a temporary, oil-based paint applied strategically to various surfaces of the car during testing sessions. Flo-vis paint is designed to visually highlight the airflow patterns over the car, providing crucial insights to engineers.
When the car is in motion, the flo-vis paint reacts to aerodynamic forces, creating streaks and patterns that indicate how air is flowing over the vehicle’s surfaces. This visual feedback aids engineers in assessing the effectiveness of aerodynamic components, such as wings and diffusers. By analyzing the paint patterns, teams can make informed adjustments to optimize the car’s aerodynamics for better performance.
In essence, the green paint serves as a real-time, on-track tool for aerodynamic testing, helping teams fine-tune their setups and gain a competitive advantage.

